
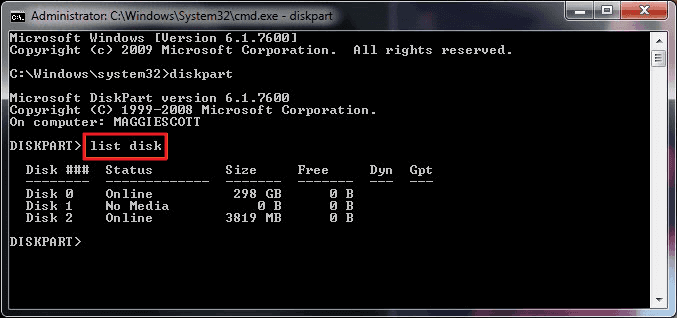
The first command we should use is list disk that should display the list of the disks currently connected to the computer:Įncrypt and password-protect files with Encryptability encryption software for Windows 11,10,8.Īgain, it's very important to properly identify the disk we want to work with in the list. This should display the DISKPART command prompt. When the command prompt window opens, start the DISKPART tool by entering the diskpart command into the command prompt window: The Ctrl+Shift combination should force the command prompt to open in the "administrator" mode. If you have an older version of Windows such as Windows 7, you can open the command prompt in the administrator mode as follows: click the Start button and enter cmd in the search box make sure that cmd is highlighted on the menu displayed, but do not press the Enter key yet instead, press the Ctrl and Shift keys together, and while keeping them depressed, press Enter.
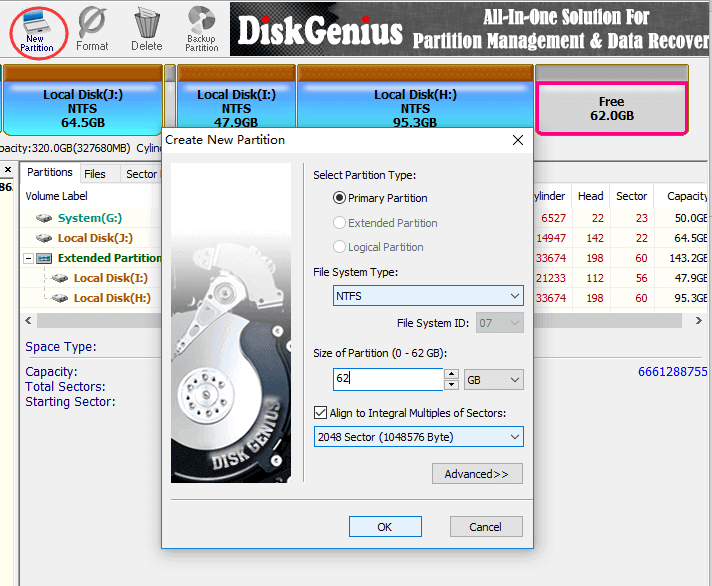
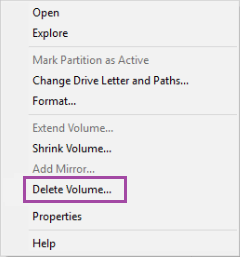
In the recent versions of Windows you can simply right-click on the Start button and choose one of the command offered: First, you need to open Windows command prompt in the "administrator" mode. The procedure of getting to the DISKPART tool is slightly different in different versions of Windows. The tricky part is, that DISKPART is a command-line tool, that requires us to type commands into its command prompt to make it do what we want. While the Disk Management tool is helpless in this situation, fortunately Windows offers another tool, DISKPART, that can do things to the disks that Disk Management can't. However, what if we want to delete the EFI system partition and re-initialize the disk from scratch? Note that it's not because the partition is EFI, it's because the tool that created that partition had marked it in a way that prohibits other tools to tamper with it. However, if we right-click on the first EFI partition, the menu we get is completely disabled:Īs you can see, the system partition is protected in such a way that even the powerful Disk Management tool cannot do anything to it. If you right-click on the normal NTFS partition, you should see the normal menu that lets you perform various tasks on that partition, including the Delete Volume command: Although these two partitions looks similar, they are treated very differently by Windows. In our case, the 240 GB disk (shown as 223.56 GB disk in the list) is Disk 3 (let's remember this number, we will need it a bit later.) It has two partitions, one is a 128MB EFI partition that has no drive letter assigned, and another NTFS partition of the size 223.43 GB, that has the label test and the drive letter G. If in doubt, better unplug all external drives except for the one you actually want to work with, to make sure you are not accidentally erasing data on a wrong disk! (Apparently, the disk manufacturers and Windows have a different understanding of what a "gigabyte" is.) Also, if you have several disks of the same size attached, it may get even more confusing. For example, in this example, a hard drive that's described as a 240 GB drive by the manufacturer, is shown to have only 223.56 GB by Windows. Usually you can do it by the total size of the disk displayed, although it may be confusing. The most important thing when using the Disk Management tool is to make sure you can identify the disk you want to manage in the list. Password-protect and hide personal files and folders with Folder Guard for Windows 11,10,8. Because with Disk Management it's very easy to destroy your partitions and lose your files, if you don't know what you are doing. If you have a newer version of Windows, right-click on the Start Menu, and choose Disk Management from the menu displayed:īefore you continue, first things first: Disk Management is a very powerful tool, and with great power comes great responsibility! If you are not very experienced with computers, you can look, but better not touch and let someone more knowledgeable to do the job. If you have Windows 7, run Windows Explorer, right-click on Computer, choose Manage from the menu, then select Disk Management under Storage.
It's easy to open Disk Management, but the procedure is slightly different in different versions of Windows. The way to do such tasks in Windows is to use the Disk Management tool that comes preinstalled with Windows. However, what if you want the drive to be prepared differently? For example, you may want to re-format the drive, or change the partitions that it has. If you've bought an external drive in a store, the preparation has probably been already done by the drive manufacturer. Encrypt and password-protect external drives with USBCrypt encryption software for Windows 11,10,8.Īs you probably know, in order to be able to store files on a hard drive, it needs to be prepared first: it needs to be initialized, partitioned, and formatted just the right way.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
